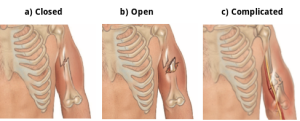
Classification of fractures
Fractures are a very common hard tissue injury and are also known as breaks. A fracture is a broken bone and comes in three (3) classifications.
A closed fracture remains inside the body and does not pierce the skin. These are the most common broken bones that occur. They are also known as simple fractures.
An open fracture is a break that does pierce the skin so that bone can be seen. These are also known as compound fractures, because there is more than one (1) issue that needs to be addressed (i.e. bleeding, open wound etc).
Complicated fractures are where the bone causes further damage to major nerves, organs or blood vessels. These are complicated because they can be life threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Types of Fracture
Although there are three (3) classifications of a fracture, there are also many different types of fractures. These are the three (3) more common types:
A complete fracture breaks clean through the bone, so that there are now two (2) parts.
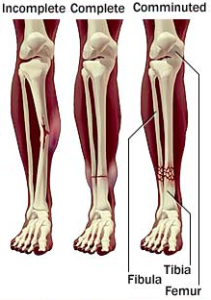
Comminuted fractures result in more than two (2) parts to the bone. This can be a smashing of bone or simply multiple fractures in the one (1) bone.
An incomplete fracture or greenstick fracture does not break the whole way through the bone, so that the bone is still in one piece, but has a break in it.
Signs and Symptoms
There are many signs (what can be seen) and symptoms (what the casualty feels or reports) of broken bones. These include:
- hearing or feeling a break
- hearing or feeling a grating of bone
- pain
- redness
- loss of function
- deformity
- bone protruding from skin (open fracture).
Management
The main aims in the management of a fracture includes:
- immobilise the area
- reduce pain
- prevent further damage
- reduce bleeding and shock
Management requires the first aider to:
- DRSABCD
- control bleeding
- cover wounds
- check for other injuries
- casualty remain still
- immobilise fracture
- handle gently
- seek medical attention