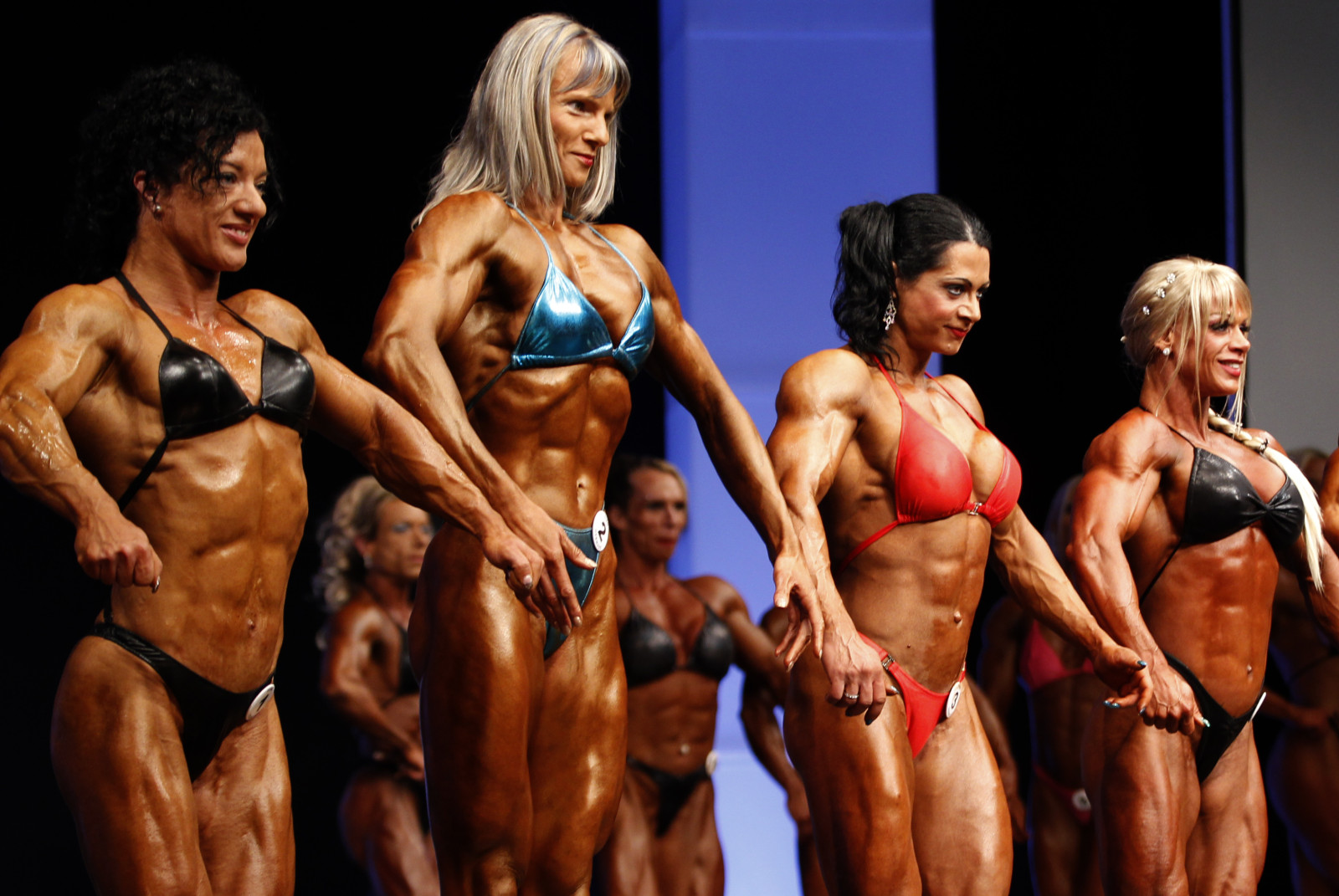
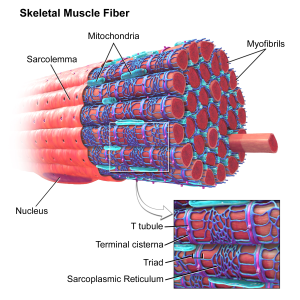
Muscular hypertrophy is an increase in the size of the muscle cross-sectional area because of an increase in myofibrils (the tissue component of the cell responsible for contraction) within the muscle cell (myocyte). A myofibril is a rod like unit within a myocyte that contracts to produce movement. The larger the myofibril, the larger the myocyte and the more force the muscle can produce.
Muscular hypertrophy results in an increase in muscular strength and muscular endurance. This helps improve performance by allowing the athlete to exert a greater force and to repeat movements more often. Often hypertrophy will also increase muscular contraction speed allowing greater power to be produced during contraction. This is very beneficial in sports that require, strength, power, or muscular endurance. Such sports include: shot put, sprinting, rugby, NFL, AFL, Ice-hockey, and martial arts.
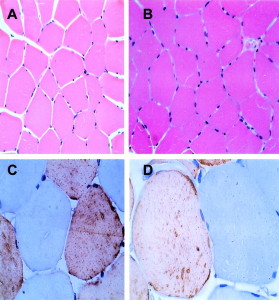
Muscular cross sectional area changes. A and C are before training, B and C are after training (and doping in this study). [1]
[1] Indrani Sinha-Hiki, et al. “Testosterone-induced increase in muscle size in healthy young men is associated with muscle fiber hypertrophy”