There are a range of protective behaviours and risk behaviours that relate to health. As you study this dash point you should make sure you are covering the 2 learn to dot points as well. They are:
- explore current research and information to:
- identify the prevalence of and trends in the health behaviours of young people
- challenge the accuracy of societal perceptions of the health behaviours of young people
- identify protective and risk behaviours for health issues relevant to young people and predict how risk decreases or increases when multiple factors interact
Prevalence and trends
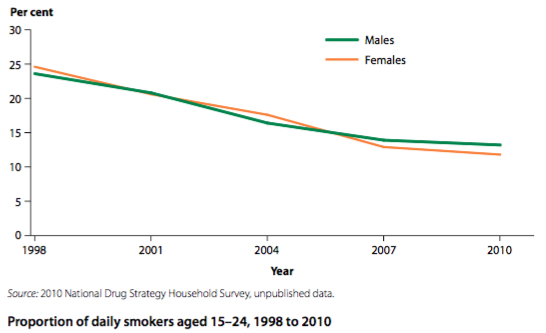
Prevalence is the total number of cases of a disease in a given population at a specific time, while a tend is whether the number of new cases (incidence) is going up or down. Currently in Australia protective behaviours and risk behaviours of young people cover a wide range of behaviours. Among young people smoking rates continue to decline, as does illicit drug use and alcohol consumption. Other protective behaviours and risk behaviours are moving in the right direction, but still have plenty of room to improve.
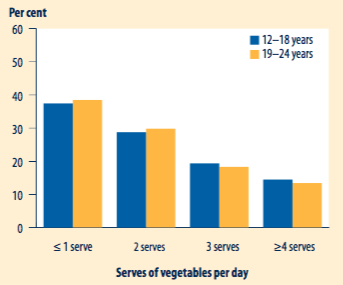
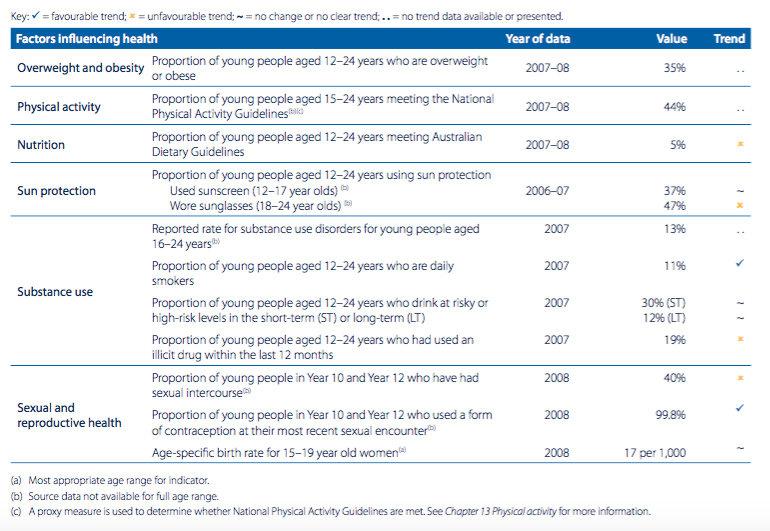
44% of young people met the physical activity guidelines; however, rates are lower in regional and remote areas, and Indigenous young people. In addition to this only 5% of young people met the daily recommended serves of both fruit and vegetables. Maintaining a healthy, varied diet prevents diseases such as cardiovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes and some types of cancer.
Currently skin cancer is the most prevalent cancer among young people. Sunscreen is the most widely used protective behaviour (37%), but still needs lots of improvement. As do the other protective behaviours.
Sexual behaviour amongst young people carries with it many risks and with chlamydia rising in young Australians it is no surprise to learn that only 2 thirds of sexually active young people us a condom.
35% of young people are also over-weight or obese. Although this number has not significantly changed since 1995, it is rising. Being overweight or obese affects young people psychologically and increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer and more.
Societal perceptions
Our society often has mis-perceptions about young people and their protective and risk behaviours. Much of this feeds from the media, which likes to pick up and run with negative stories. many of these stories portray young people as taking high risks as they:- get drunk every weekend
- take illicit drugs, particularly ice
- drag race and speed in their cars
- bully and abuse, or
- participate in sexting and pornography
Relevant health issues
A number of relevant health issues for young people are mentioned in the syllabus. This list includes: food habits, body image, physical activity, drug use, mental health, sexual health and road safety. You are required to identify protective behaviours and risk behaviours for these issues and how the combination of these behaviours increases or decreases the risk. For example, risk behaviours for sexual health include:- becoming sexually active
- watching pornography
- not using a condom
- combining drugs, or alcohol with sexual activity
- sexting, or using media (photos, videos, etc) to record sexual activity
- anal sex
[1]
Protective behaviours include:
- abstinence
- sexual education
- having respectful relationships with the opposite sex
- barrier method contraceptions